*Editor’s note: The number of global Hallyu (Korean Wave) fans is approaching approximately 225 million, according to the 2024 report by the Korea Foundation. The surge in fans marks the dawn of the "Digital Silk Road" era, where communication transcends the limitations of time and space, enabling real-time interaction across the globe. Truly, we are in the era of "Hallyu 4.0."
K-Medical and Muslim Patients
Contributed by Suk Soo-sun (professor at Yonsei Graduate School of Communication & Arts)

◇ Design Strategies for Attracting Muslim Patients in South Korea's Medical Tourism Industry
The healthcare service industry has emerged as a high-value sector leading the global economy in the 21st century, thanks to the advancements in information and communication technology, transportation, and cutting-edge medical technologies.
Medical tourism, in particular, is a high-value service industry with significant economic ripple effects and growth potential, prompting governments and companies worldwide to pursue various policies.
 |
| ▲ Seoul Mayor Oh Se-hoon and key guests pose for a commemorative photo at the opening ceremony of the 2023 Seoul International Travel Mart for Medical Tourism (SITMMT 2023) held at Sofitel Ambassador Seoul in Songpa-gu, Seoul, on September 5, 2023. (Yonhap) |
South Korea's medical services are relatively affordable compared to those in developed countries and boast top-tier expertise based on excellent human resources, setting the stage for the growth of the medical tourism industry. The steady increase in inbound tourists since 2005, driven by the Korean Wave (Hallyu), economic exchanges, and enhanced tourism recognition, is now evolving into a medical tourism boom.
Despite the surge in Middle Eastern medical tourists visiting Korea, the awareness of Korean medical services remains low. Institutional issues, cultural differences, and a lack of promotion have resulted in lower performance compared to competitors. Given that Middle Eastern Muslim medical tourists tend to stay longer and travel in larger groups, personalized marketing strategies are essential to attract these high-income visitors.
 |
| ▲ Opening of the Busan International Medical Tourism Convention with 100 companies from 13 countries participating. (Yonhap) |
With increasing national income and life expectancy, as well as long domestic wait times and high medical costs, more patients are seeking medical tourism. Competition among Asian countries, where medical costs are lower and facilities are well-equipped, is fierce.
South Korea's medical services, with their advanced ICT and big data-based services, present promising growth potential. Designated as one of the '17 New Growth Engine Industries' in January 2009, the country introduced medical tourism visas and various government and corporate policies to promote the sector.
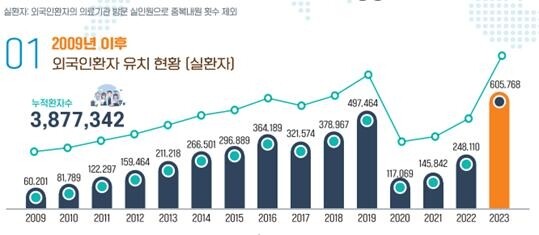 |
| ▲ 2009-2023 Foreign Patient Attraction Performance (Ministry of Health and Welfare) Source: e-Nara Index (Korea Tourism Statistics) |
Expanding the target countries for foreign patient inflows beyond China to include Indonesia, Vietnam, Russia, Mongolia, and the Arab regions is crucial for sustained growth in medical tourism.
◇Characteristics of Muslim Patients
The Arab region, with its high population growth rate, Westernized dietary habits, and hot climate, faces a surge in chronic diseases like obesity, hypertension, and diabetes. However, the region's medical infrastructure is severely lacking, increasing dependency on overseas medical services.
In the UAE, for instance, overseas medical tourism is a common practice among its citizens, with over 130,000 people traveling abroad for treatment annually. The UAE government supports these expenses, but awareness of Korean medical services remains low, with a preference for culturally similar Muslim countries or geographically closer European regions.
Given the strong market potential, especially among the Muslim population, and their significant economic power, attracting VIP-level medical tourists who often travel with families and stay for extended periods is a priority.
 |
| ▲ This Yonhap file photo shows Muslim tourists traveling in Korea. (Yonhap) |
The population of Islamic countries tends to be younger, driven by high birth rates, and as more young people pursue education and enter the workforce, their incomes are rising, leading to a steady increase in spending on tourism.
While the number of Muslim medical tourists visiting Korea still lags behind that of Chinese or Japanese tourists, Muslim patients who come for treatment often travel with their families and stay for extended periods, making them high-spending VIP-level tourists.
The strong communal ties within Muslim communities mean that successfully treating a prominent royal or wealthy individual can lead to thousands more visiting the hospital, underscoring the importance of initial engagement. These patients often share a patriarchal tradition with strong family values, similar to Eastern cultures like Korea's. The family takes responsibility for the patient, sometimes appearing overprotective, reflecting their deep concern for the patient's well-being.
Religious beliefs play a significant role, with many Muslims viewing illness and healing as part of God's will. Patients may communicate their pain openly with family members but less so with medical staff, potentially leading to differences in the perceived effectiveness of pain management. Since many Muslims are accustomed to European-style medical care, fostering mutual understanding and trust through communication and explanation is crucial for attracting these patients.
However, institutional challenges, cultural differences, and a lack of promotional efforts have limited the success of major Korean healthcare facilities in attracting medical tourists from Muslim-majority regions.
◇ Key Elements for Enhancing International Medical Services
Medical tourism involves not only the process of receiving healthcare services at a specific medical institution but also encompasses the broader experience of the country, region, climate, culture, and amenities where the institution is located. As such, it is an act of consuming a comprehensive package of services.
Medical services are high-involvement services where patients are deeply concerned about the outcomes. However, when treatment results are similar, patients tend to focus more on the convenience and comfort during the treatment process. Therefore, patient experience is a critical issue in medical services. Strategies to enhance satisfaction among international patients from diverse cultural backgrounds include involving patients directly in the service delivery process.
Understanding and addressing cultural differences—such as language, religion, customs, and lifestyle—are essential when dealing with patients. Service management should prioritize identifying and fulfilling the specific needs and preferences of patients from different cultures.
The medical industry is characterized by a unique relationship where the service provider holds significant control over the process. This necessitates an innovative shift towards customer-centered thinking. Even with advanced medical technology, the likelihood of success diminishes if the provider fails to establish a rapport with the patient. As a result, research on service design, particularly "design thinking" in healthcare services, is gaining attention.
As the trend of "servitization"—the commercialization of services combined with products—accelerates, the focus in healthcare has shifted from solely medical technology or traditional management perspectives to providing patients with a high-quality medical service experience. The need for service design research, which emphasizes human-centered design methods, has emerged as crucial in the healthcare sector, where human dignity must be preserved.
In addition to providing medical treatment, hospitals should create an environment that showcases their cultural sensibilities, helping patients heal in body, mind, and spirit. Ensuring that these elements translate into positive patient experiences is vital.
 |
| ▲ This file photo shows a muslim-friendly restaurant in Korea. (Yonhap) |
Rather than segregating medical and tourism sectors, there should be a paradigm shift towards viewing them as an integrated, unified industry. Hence, instead of marketing solely on advanced medical technology or competitive pricing, there is a need to develop products with a common theme and implement integrated marketing strategies. Medical tourism institutions must continually identify and promote elements that instill trust in medical tourists and improve service quality.
◇ Design Strategies to Attract Muslim Patients
South Korea has been promoting its strengths as a medical tourism destination globally at a national level.
To establish a new image of "Korea as a medical powerhouse," comprehensive manuals and promotional booklets covering domestic medical services and tourism guides have been created and distributed. Additionally, multilingual medical tourism websites have been developed and operated as part of a broader promotional effort. However, the content of these promotional materials and websites has often been inadequate, with incomplete information and only partial translations into other languages. There is a need to redesign these resources in a way that makes them more user-friendly and easily accessible to those who need the information.
 |
| ▲ This poster, provided by the Korean Food Foundation, shows the "Halal Restaurant Certification Guidebook." (PHOTO NOT FOR SALE) (Yonhap) |
Among the issues identified in providing medical services to visiting Muslim patients, three key areas urgently require improvement.
First, communication is critical in delivering medical services, as it is essential to build trust and provide a sense of security to patients. However, when communication barriers exist, there is a high risk of complications during treatment. Differences in cultural background, language, or gender between medical staff and patients can lead to challenges in accurately expressing symptoms or understanding pain, which makes proper diagnosis and treatment more difficult. These communication issues can cause significant uncertainty, anxiety, and stress for both patients and medical professionals.
Lastly, religious and cultural differences can pose challenges.
For Muslims, Islam is more than just a religion; it is a way of life and a philosophy. Therefore, understanding Islamic culture is crucial for improving service satisfaction. This includes providing 'Halal' meals for patients, establishing prayer rooms within hospitals, installing Arab TV channels, and ensuring compliance with Islamic laws. These adaptations to the hospital environment, tailored to the cultural needs of local Muslim populations, are vital elements in enhancing their overall experience.
However, due to the relatively small Muslim population in Korea, there is a shortage of facilities such as prayer rooms and specialized restaurants catering to Muslim needs. The current amenities available to visiting Muslim tourists are rather limited.
 |
| ▲ This Yonhap file photo hsows a muslim prayer room established in a department store. (Yonhap) |
Some facilities have begun expanding their services to include prayer spaces with washing facilities for pre-prayer ablutions, as well as compasses and carpets to help Muslims align their prayers towards Mecca. Despite these efforts, most prayer rooms are set up merely as spaces, without consideration for the religious significance and atmosphere required for such a sacred practice. These spaces need to be improved to provide a more sacred and comfortable environment for prayer.
The Korea Tourism Organization provides a restaurant guidebook for Muslim tourists, informational materials for Islamic communities, and resources on prayer rooms across the country. However, there is a general consensus that it is somewhat challenging to carry these materials and find the desired information.
The significant differences in dietary practices due to religion can also impact the effectiveness of disease treatment, necessitating more careful consideration and preparation in the meals and supplies provided to foreign patients undergoing hospitalization abroad.
It is essential to recognize the need for developing meal plans and guidelines for Muslim patients to minimize dissatisfaction with food, as well as establishing a foundation for meal services for foreign patients that includes diverse menu options based on different countries. This requires a proactive approach to addressing the challenges faced by patients during their treatment related to dietary preferences, considering cultural understanding and food usage.
Additionally, providing opportunities to learn about Korean culture can help supplement the limited variety in the diets of foreign patients. This can be achieved through the operation of Korean restaurants, Korean food experiences, and the provision of Halal food, thereby narrowing the gap with Muslim patients. Continuous attention to the religious and cultural uniqueness of Muslims in Korea is necessary, along with strategies to appropriately respond to the differences arising from cultural diversity.
To secure a competitive advantage in the increasingly fierce international medical service industry, there is a need to develop differentiated medical tourism products compared to competing countries and to provide experiential value that meets the needs of locals through effective service design. Despite a quantitative increase in academic research on medical tourism driven by social, cultural, and economic factors, most studies focus primarily on conceptual understanding or simple comparisons with international cases.
There is a significant lack of research related to international medical services that addresses policy measures targeted at specific markets and responds to consumer demands.
To attract foreign patients and revitalize medical tourism, it is crucial to incorporate design concepts into this field, enabling the rapid identification and execution of opportunities with creative and integrated capabilities. Recognizing the importance of design capabilities and understanding the systems and applied technologies needed to adapt to constantly changing media is vital.
At this point, it is essential to establish practical measures that can enhance the competitiveness of medical institutions and revitalize Korean medical tourism through a complex thinking ability that integrates design thinking and specialized knowledge to approach problems from various angles.
(C) Yonhap News Agency. All Rights Reserved























